Java-객체지향 프로그래밍 상속
상속
객체지향 프로그래밍의 대표요소 중 상속에 대해서 알아보자.
자바에서 상속이란, “현실에서 부모가 자식에게 재산을 상속한다”와 같이 무언가를 물려준다는 개념이다.
- 자바에서는 무엇이 무엇에게 상속하고 물려줄까??
-> 클래스에서 클래스간의 상속이다.
자바에서는 부모(상위)클래스와 자식(하위)클래스가 존재하며, 부모클래스는 자식클래스에게 상속해준다.
- 부모클래스는 자식클래스에게 무엇을 상속하나요?
-> 부모클래스는 자식클래스에게 부모클래스에 정의된 필드와 메서드를 상속받는다.
위에서 설명한 상속의 개념을 바탕으로 코드로 확인해보자.
상속-코드예시
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
class Human{
String name;
int age;
String gender;
void eat(){
System.out.println("밥을 먹습니다.");
}
void sleep(){
System.out.println("잠을 잡니다.");
}
void walk(){
System.out.println("걷습니다.");
}
}
class Student extends Human{ //Human클래스 상속
String schoolName;
void study(){
System.out.println("공부를 합니다.");
}
}
class Singer extends Human{ //Human클래스 상속
String groupName;
void sing(){
System.out.println("노래를 합니다.");
}
}
class Programmer extends Human { //Human클래스 상속
String companyName;
void coding(){
System.out.println("코딩을 합니다.");
};
}
public class InheritanceExample{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Human h = new Human();
h.name = "홍길동";
h.age = 30;
h.gender = "male";
h.sleep();
h.eat();
System.out.println(h.name);
Singer s = new Singer();
s.name = "김싱어";
s.age = 24;
s.gender = "female";
s.sleep();
s.sing();
System.out.println(s.name);
}
}
//출력
잠을 잡니다.
밥을 먹습니다.
홍길동
잠을 잡니다.
노래를 합니다.
김싱어
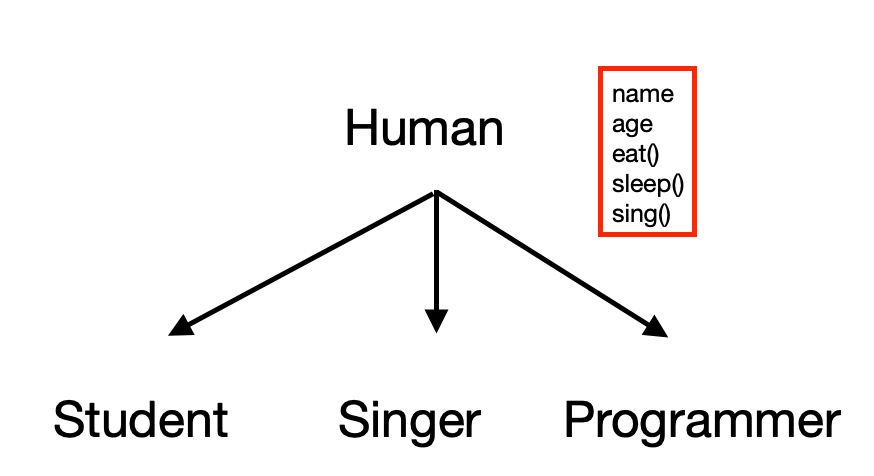
위의 코드와 그림처럼 학생,가수,프로그래머는 모두 사람이다.
따라서, 사람은 부모클래스 나머지 학생,가수,프로그래머는 자식클래스로 사용한 것이다.
Student,Singer,Programmer은 extends 키워드를 통해 Human이라는 상위 클래스의 필드와 메서드를 상속받을수 있으며, 상속받은 하위 클래스들은 각자의 필드와 메서드에 상위 클래스의 필드와 메서드가 선언되어 있지않지만, 부모클래스의 필드와 메서드를 사용할 수 있다.
만약 상속이 없었더라면 name,age와 같은 공통의 필드나 메서드들을 모두 선언해주어야하며, 계속해서 중복된 코드를 작성해야하는 번거로움이 생겼을 것이다.
자바에서 상속은 단일 상속(Single Inheritance)만을 허용하며, 하나의 클래스는 하나의 클래스만 상속받을 수 있다.라는 의미이다.
메서드 오버라이딩(Method Overridng)
메서드 오버라이딩이랑 상위클래스로부터 상속받은 메서드들을 하위클래스에서 동일한 이름의 메서드를 재 정의 하는 것이다.
코드를 통해 한번 살펴보자
class Human{
String name;
int age;
String gender;
void eat(){
System.out.println("밥을 먹습니다.");
}
void sleep(){
System.out.println("잠을 잡니다.");
}
void walk(){
System.out.println("걷습니다.");
}
}
class Student extends Human{
String schoolName;
void study(){
System.out.println("공부를 합니다.");
}
void eat(){ //메서드 오버라이딩
System.out.println("짜장면을 먹습니다.");
}
}
class Singer extends Human{ //Human클래스 상속
String groupName;
void sing(){
System.out.println("노래를 합니다.");
}
void eat(){ //메서드 오버라이딩
System.out.println("짬뽕을 먹습니다.");
}
}
class Programmer extends Human { //Human클래스 상속
String companyName;
void coding(){
System.out.println("코딩을 합니다.");
}
void eat(){ //메서드 오버라이딩
System.out.println("탕수육을 먹습니다.");
}
}
public class InheritanceExample{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Human h = new Human();
Singer s = new Singer();
Programmer p = new Programmer();
h.eat();
s.eat();
p.eat();
}
}
//출력
밥을 먹습니다. (Human)
짬뽕을 먹습니다. (Singer)
탕수육을 먹습니다. (Programmer)
위의 코드처럼 각각의 하위 클래스들은 상위클래스의 메서드를 오버라이딩 하고 있다.
다만, 메서드 오버라이딩 시에는 세가지 조건을 만족시켜야만 사용할 수있다.
- 메서드의 요소(메서드 이름, 매개변수, 반환타입)이 상위 클래스의 메서드와 완전히 일치 해야한다.
- 접근 제어자의 범위가 상위 클래스의 메서드 보다 같거나 넓어야 한다.
- 예외는 상위 클래스의 메서드보다 많이 선언할 수 없다.
super 과 super()
super과 super는 기존의 클래스 생성자 및 객체 호출과 동일하다. 다만, 자기자신의 필드와 생성자를 호출하는 것이 아닌 부모클래스의 필드와 생성자를 호출 하는 것이다.
class Human{
int age = 10;
}
class Programmer extends Human {
int age = 5;
void printAge(){
System.out.println("age = " + age);
System.out.println("this.age = " + this.age);
System.out.println("super.age = " + super.age);
}
}
public class InheritanceExample{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Programmer p = new Programmer();
p.printAge();
}
}
//출력
age = 5
this.age = 5
super.age = 10
위 코드에는 상위,하위 클래스 모두 필드에 같은 age라는 변수가 선언이 되어있다.
이를 구분하기 위하여 super키워드를 사용하면 상위클래스의 필드값으로 인식하고, super키워드가 없다면, 자신이 속한 객체에서 필드값을 참조한다.
다음으로 super()를 알아보자.
class Human{
int age = 10;
Human(){
System.out.println("휴먼 클래스 생성자");
}
}
class Programmer extends Human {
Programmer(){
super();
System.out.println("프로그래머 클래스 생성자");
}
}
public class InheritanceExample{
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Programmer p = new Programmer();
}
}
//출력
휴먼 클래스 생성자
프로그래머 클래스 생성자
위 super()키워드는 this()와 동일하게, 생성자를 호출할 때 사용한다.
다만, 차이점은 this()는 같은 클래스의 다른 생성자를 호출 하지만 super()는 상위 클래스를 호출하는 차이 점이 있다.
정리
- 자바에서 상속은 부모클래스의 필드와 메서드를 자식클래스가 물려받는 것
extends키워드를 통해 부모클래스를 통한 상속을 할 수 있다.
- 자식클래스는 부모클래스의 메서드를 오버라이딩해서 사용할 수 있다.
- 오버라이딩을 위해서는 3가지 조건을 지켜야한다.(메서드 요소 일치, 접근제어자 범위, 예외 선언 개수)
super,super()키워드를 통해 부모클래스의 필드값과 생성자를 호출할 수 있다.- 자바의 상속을 이용하면, 불필요한 코드를 줄이고 가독성을 높일 수 있다.